Using https://vacuum-calculator.pfeiffer-vacuum.com and the previous post's volume and surface area data, I have some inital impressions of our pump requirements for the 8 m long interferometer.
Other assumptions:
Desoprtion: 1e-9 mbar*l/(s*cm²)
Leak rate: 3e-9 mbar*l/s
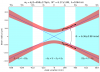
1. Our final pressure limitation will be a function of desorption, not leak rate, because our surface area is so huge
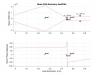
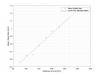
2. The time to reach 6 Torr, where Pfeiffer starts the turbos, is given approximately by 1 hr * (4.3 m^3/h rougher pumping speed / pump roughing speed)
3.
A. 3 HiPace 80 DN 63 get to a pressure of 10^-7 Torr in 12 hours, 10^-8 Torr in a week
B. 1 HiPace 80 DN 63 gets to a pressure of 10^-7 Torr in 36 hours, 5*10^-8 Torr in a week
4. A 1 m, 6.45 mm tube between the roughers and the turbos doesn't greatly affect the pump down time or the final pressure